from Along the Watchtower blog:
Longtime readers will recall that we've had several conversations here regarding the impact that the Fed's quantitative easing policy is having on the costs of everyday food items. Soaring prices of agricultural commodities are going to continue to have a devastating effect on the purchasing power of average Americans and consumers around the globe. Since prices have now recovered some from the selloffs after the Japanese earthquake and tsunami and since there is no end in sight to QE, I thought it was time to once again take a look at out favorite commodities and assess where their prices may be headed over the spring and summer.
Let's start with the grains because rising grain prices cause all sorts of inflation. Not only are grains the raw input to countless consumer goods, grains are also the primary foodstuff for cattle ranchers and hog finishers as they prepare their herds for slaughter. Let's start with wheat, which is being influenced not just by the falling dollar. Price is also feeling the impact of the ongoing drought in the "winter wheat zone" of the high plains of Kansas, Oklahoma and Texas.
http://www.bloomberg.com/news/2011-03-24/worst-texas-drought-in-44-years-eroding-wheat-beef-supply-as-food-rallies.html
Now take a look at the chart. Long-term support held at $7.50 and wheat looks almost certain to catapult higher very soon.
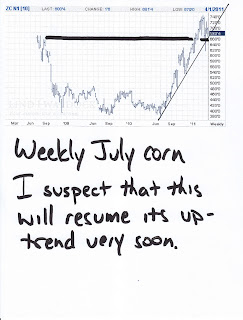
Now here's the deal with corn...it's expensive to grow! The primary fertilizer that Midwestern corn farmers utilize is anhydrous ammonia. Last year, anhydrous ammonia cost your average farmer about $425/ton. This year, the cost has almost doubled to $750-800/ton. So, while it might be tempting to seed a lot of acres with corn to capitalize on the high price, the input and production costs are so high that many farmers will choose to plant soybeans, instead. Less acres of corn planted lead directly to less production. Less production leads directly to even higher prices. (Remember that below when we get to cattle.)
So what about soybeans? Soybeans are the one grain that I don't expect to rise in price. They will, most likely, stay rangebound through the summer. Why? Besides the fertilizer costs affecting plantings, soybeans get extra acreage for another reason: Weather. Because soybeans have a shorter growing season, they are a "fall back plan" for many farmers who struggled to get corn planted due to overly wet spring conditions.
http://www.galesburg.com/news/x1777821638/Galesburgs-spring-outlook-cool-and-wet
If the upper Midwest spring turns out cool and wet, many farmers will forego corn planting and turn, instead, to soybeans. Extra supply = Lower cost.
Now, let's get back to corn. Have you ever heard the term "corn-fed beef"? Most of the best steakhouses proudly champion corn-fed beef because, frankly, its tastes a helluva lot better than grass-fed. The high sugar content of the corn gets converted into fat. The fat makes its way into the muscle and you, Mr. Steakeater, get yourself a beautiful, marbled "prime" steak. Fat cows are also desirable at slaughter because, well, they weigh more and cattle are sold by the pound. OK, so now, pretend for a moment that you're a cattle rancher. As your cattle are growing and being prepared for market (the term is "finished"), you want to feed them as much corn as they'll eat and you can afford. Corn at $7.00/bushel really cramps your business plan. Your first reaction is to control costs by thinning your herd, i.e. you sell some prematurely, before they are "finished". You might also simply want to sell some of your herd to take advantage of today's high prices.
http://www.saljournal.com/news/story/Cattle-prices-32411
Either way, this extra supply in the short term has actually worked to keep cattle prices from soaring at the same rate as the grains. But this is temporary. By this summer, supply will decrease as cattle that would have been coming to market just then have already been slaughtered. Are we already beginning to see this play out on the chart? Well, take a look: